What is a business model?
An e-commerce business model is a framework that outlines how an online business operates, generates revenue, and serves its customers. It defines the structure and strategies of the business in the digital realm.
Why are business models important?
Business models are essential for both new and established businesses. They help companies understand their customers, keep employees motivated, attract investment, and provide a sustainable competitive advantage by identifying growth opportunities.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C):
- In this model, businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers.
- Examples include online retail stores like Amazon, fashion e-commerce sites, and food delivery services.
Business-to-Business (B2B):
- B2B e-commerce involves companies selling products or services to other businesses.
- Examples include wholesale suppliers, software as a service (SaaS) providers, and office supply companies.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C):
- C2C e-commerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers.
- Online marketplaces like eBay and classified ads platforms fall into this category.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C):
- D2C brands manufacture and sell their products directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels.
- Examples include Casper (mattresses) and Warby Parker (eyeglasses).
Subscription Model:
- Businesses offer products or services on a subscription basis, often with recurring payments.
- Companies like Netflix, Spotify, and subscription box services use this model.
Marketplace Model:
- Marketplaces bring together multiple sellers and buyers on a single platform.
- Amazon, eBay, and Etsy are well-known examples.
Crowdsourcing Model:
- Crowdsourcing platforms allow businesses and individuals to raise funds, gather ideas, or collaborate on projects.
- Kickstarter and Indiegogo are examples of crowdsourcing platforms.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P):
- P2P e-commerce connects individuals for sharing resources or services, often on a temporary basis.
- Airbnb, Uber, and sharing economy businesses fall into this category.
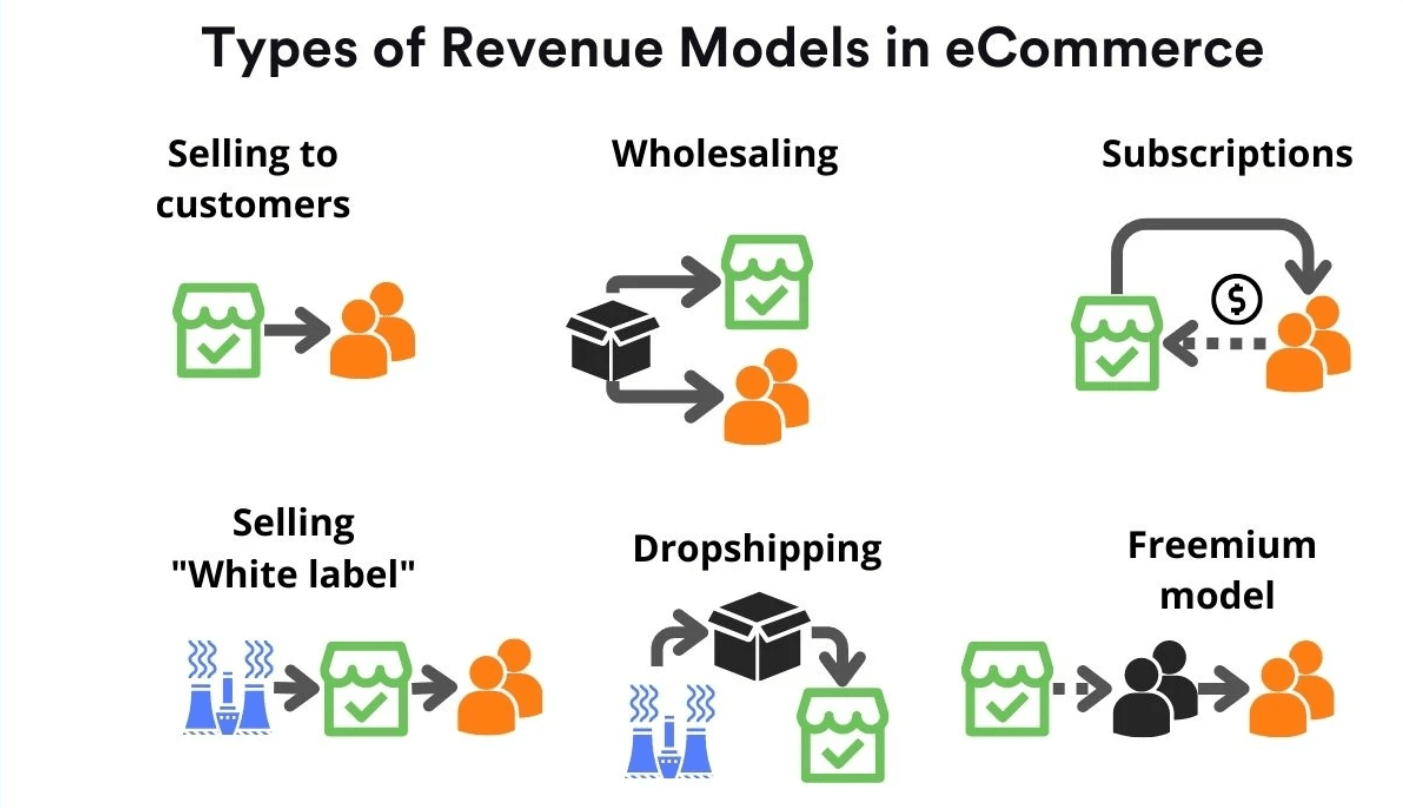
Wholesale and Manufacturing:
- Some e-commerce businesses act as wholesalers or manufacturers, selling products in bulk to other businesses.
- These businesses typically serve as suppliers for retailers.
Dropshipping:
In the dropshipping model, online retailers don’t keep products in stock but instead transfer customer orders and shipment details to the manufacturer or another retailer who ships the products directly to the customer.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketers promote products or services on their websites and earn a commission for each sale or lead generated through their referral links.
E-commerce business models may incorporate one or more of these approaches.
Selecting the right model depends on factors like the nature of products or services, target audience, competitive landscape, and revenue generation strategies. The choice of model also impacts how the business handles logistics, customer service, marketing, and other key aspects of e-commerce operations.
Let’s get started
Are you looking for E-commerce Development ?
- Dedicated IT Expert Team
- Certified Developers
- Quality Assurance
- Handle Tight Deadlines
- Handover Source Code